Vaginal bleeding outcome in the third trimester of pregnancy
Abstract
Background and Aim: Maternal mortality form APH has reduced considerably in the last three decades due to improvements in obstetric care and blood transfusion services. Hence the purpose of the study was to study fetal and maternal outcomes in cases of third trimester vaginal bleeding.
Materials and Methods: The study was conducted at the Institute of Medical Sciences. During this study period, 450 cases had an antepartum hemorrhage. All patients who came with a history of bleeding per vagina after 28 weeks of gestation were hospitalized. Cases with bleeding per vagina after 28 weeks of gestation were included in the study.
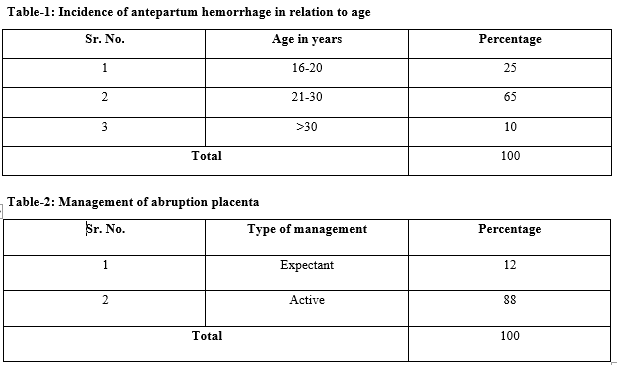
Results: Out of total cases of the abrupt placenta, 12 percent cases were managed expectantly,8 cases delivered within 6 days and 6 cases reached term and delivered vaginally and 89 (88 percent) cases were managed actively.
Conclusion: At the level of a tertiary center, early recognition cause of APH, aggressive expectant management and termination of pregnancy after recording lung maturity, decrease in unnecessary C/S, good neonatal intensive care unit, active management of ideal cases will help in the improved outcome of maternal and perinatal outcome in antepartum hemorrhage.
Downloads
References
Pratt DS, Kaplan MM: Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme results in asymptomatic patients. New Eng J Med. 2000;342(17):1266-1271. doi: https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200004273421707.
Rayburn WF: Prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and induction of labor: a critical analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989;160(3):529-534. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9378(89)80020-1.
Sakornbut E, Leeman L, Fontaine P. Late pregnancy bleeding. Am Fam Physician. 2007;75(8):1199-1206.
Chilaka VN, Konje JC, Clarke S, Taylor DJ. Practice observed: is speculum examination on admission a necessary procedure in the management of all cases of antepartum haemorrhage? J Obstet Gynaecol. 2000;20(4):396-398. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01443610050112057.
Dhanalakshmi K: Outcome of pregnancy in third trimester vaginal bleeding. 2011.
Jacobsson B, Hagberg G, Hagberg B, Ladfors L, Niklasson A, Hagberg H: Cerebral palsy in preterm infants: a population‐based case‐control study of antenatal and intrapartal risk factors. Acta Paediat. 2002;91(8):946-951. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2002.tb02860.x.
Tinker, Anne G.. 1998. Improving women's health in Pakistan (English). Health, nutrition, and population series. Washington, D.C.: The World Bank. Available at http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/225041468757537910/Improving-womens-health-in-Pakistan.
Siddiqui F, Kean L. Intrauterine fetal death, Obstetrics. Gynaecology and Reproductive Medicine. 2009;19(1):1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ogrm.2008.09.007.
Weiss JL, Malone FD, Emig D, Ball RH, Nyberg DA, Comstock CH, et al. Obesity, obstetric complications and cesarean delivery rate a population-based screening study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;190(4):1091-1097. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2003.09.058.
Tuzovic L: Complete versus incomplete placenta previa and obstetric outcome. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2006, 93(2):110-117. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2006.02.006.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

