HIV/AIDS awareness in newly married females coming in OPD of a Medical College Hospital
Abstract
Objective: To assess the awareness of HIV/AIDS in newly married females coming in Gynaecology OPD of a Medical College Hospital and to devise strategies for future programmes.
Methodology: 11 villages and urban population around our hospital were taken for study. Newly married females coming in Gynaecology OPD for various complaints were surveyed. The females were asked to fill a pre-designed Performa, which included multiple choice questions.
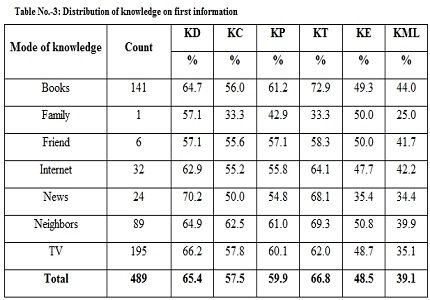
Results: In our study 489 patients were assessed. 65.4% women had knowledge about disease, 57.5% knew about complications of disease, 59.9% had knowledge about prevention of disease, 66.8% were aware about treatment of disease, 48.5% had knowledge about etiology of disease and 39.1% were aware about medico legal aspect of disease.
Conclusion: The study showed tremendous lacunae in awareness of HIV/AIDS. There is a need for evolving information, education, and communication strategies to focus on raising awareness on RH and gender related issues. A sociocultural research is needed to find the right kind of sexual health services for these young girls.
Downloads
References
2. Satpathy SK, Shaukat M. HIV/AIDS in India-The present scenario. New Delhi, National AIDS Control Organization (NACO), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, 1997:1-4.
3. Cohen MS. Sexually transmitted diseases enhance HIV transmission: No longer a hypothesis. Lancet 1998;351 (SuppI3):5-7). [PubMed]
4. Jejeebhoy SJ. Adolescent sexual and reproductive behavior: a review of the evidence from India. Social Science & Medicine. 1998 Mar 20;46(10):1275-90.
5. Smith KP, Watkins SC. Perceptions of risk and strategies for prevention: responses to HIV/AIDS in ruralMalawi. Soc Sci Med.2005Feb;60(3):649-60. [PubMed]
6. Santhya KG, Jejeebhoy SJ. Early marriage and HIV/AIDS: risk factors among young women in India. Economic and Political Weekly. 2007 Apr 7:1291-7.
7. Santhya KG, Jejeebhoy SJ. Sexual and reproductive health needs of married adolescent girls. Economic and Political Weekly. 2003 Oct 11:4370-7.
8. Pallikadavath S, Garda L, Apte H, Freedman J, Stones RW. HIV/AIDS in ruralIndia: context and health careneeds. J Biosoc Sci.2005Sep;37(5):641-55. [PubMed]
9. Bracher M, Santow G, Watkins S. " Moving" and Marrying: Modelling HIV Infection among Newly-weds in Malawi. Demographic Research. 2003 Sep 19;1:207-46.
10. Nath A. HIV/AIDS and Indian youth-a review of the literature (1980-2008). SAHARA: Journal of Social Aspects of HIV/AIDS Research Alliance. 2009 Mar 1;6(1):2-8. [PubMed]
11. Tuladhar H, Marahatta R. Awareness and practice of family planningmethods in womenattendinggyneOPD at NepalMedicalCollegeTeaching Hospital. Nepal Med Coll J. 2008 Sep;10(3):184-91. [PubMed]
12. UNICEF., Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS., World Health Organization. Young people and HIV/AIDS: Opportunity in crisis. The Stationery Office; 2002.
13. Naik E, Karpur A, Taylor R, Ramaswami B, Ramachandra S, Balasubramaniam B, Galwankar S, Sinnott J, Nabukera S, Salihu HM. Rural Indian tribal communities: an emerging high-risk group for HIV/AIDS. BMC International Health and Human Rights. 2005 Dec;5(1):1.
14. Mullany LC, Maung C, Beyrer C. HIV/AIDSknowledge, attitudes, and practices among Burmesemigrantfactoryworkers in TakProvince, Thailand. AIDS Care.2003Feb;15(1):63-70. [PubMed]
15. Rakwar J, Kidula N, Fonck K, Kirui P, Ndinya-Achola J, Temmerman M. HIV/STD: the women to blame? Knowledge and attitudes among STD clinic attendees in the second decade of HIV/AIDS. International journal of STD & AIDS. 1999 Aug;10(8):543-7.
16. Kunte A, Misra V, Paranjape R, Mansukhani N. HIV seroprevalence & awareness about AIDS among pregnant women in rural areas of Pune district, Maharashtra, India. Indian Journal of Medical Research. 1999 Oct 1;110:115.
17. Clark S, Bruce J, Dude A. Protecting young women from HIV/AIDS: the case against child and adolescent marriage. International family planning perspectives. 2006 Jun 1:79-88.
Copyright (c) 2018 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

