The prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency in pregnancy and neonatal outcomes
Gayam S.1*, Fatima S.2, Neelima C.3, Rani G.4
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/joog.2020.i04.03
1* Susheela Gayam, Head of Department, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Vijay Marie Hospital and Educational Society, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
2 Summaya Fatima, Registrar, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Vijay Marie Hospital and Educational Society, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
3 Neelima C, Senior Consultant, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Vijay Marie Hospital and Educational Society, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
4 Geeta Rani, Junior Consultant, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Vijay Marie Hospital and Educational Society, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
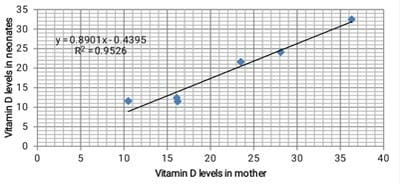
Introduction: Vitamin D is an essential fat-soluble vitamin and has multiple functions. It affects calcium metabolism, modulates the immune system, cell proliferation, and differentiation. Objective: To study the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in pregnant women and neonatal outcome in a tertiary care hospital, to study the association between maternal vitamin D and medical disorders, and to correlate maternal vitamin D deficiency with neonatal vitamin D levels and neonatal outcomes. Materials and Methods: This cross-sectional and observational study was conducted over a period of one year on 355 antenatal women admitted for safe confinement. 4 ML of whole blood was collected from median ante-cubital fossa and vitamin D levels were assessed using ELFA [Enzyme Linked Fluorescent Assay] following delivery, and 2ml of cord blood was also collected and sent for Vitamin D levels. Results: Out of the total study population, 12.96% (46) had adequate levels of vitamin D, the majority - 74.65% (265) had insufficient vitamin D levels, and 12.39% (44) had severe vitamin D deficiency. The overall deficiency among neonates was 95.22%. No significant association was found between vitamin D deficiency and maternal complications, except for the mode of delivery which was statistically significant with a P-value of 0.04. Conclusion: This study reaffirms that vitamin D deficiency is on the increase and therefore needs intervention by biochemical screening and corrective measures during pregnancy.
Keywords: Vitamin D deficiency, Prevalence, Pregnancy, Maternal outcomes, Neonatal outcomes
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Head of Department, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Vijay Marie Hospital and Educational Society, Hyderabad, Telangana, India. Email: |
Gayam S, Fatima S, Neelima C, Rani G. The prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency in pregnancy and neonatal outcomes. Obs Gyne Review J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;6(4):85-90. Available From https://obstetrics.medresearch.in/index.php/joog/article/view/116 |


 ©
©